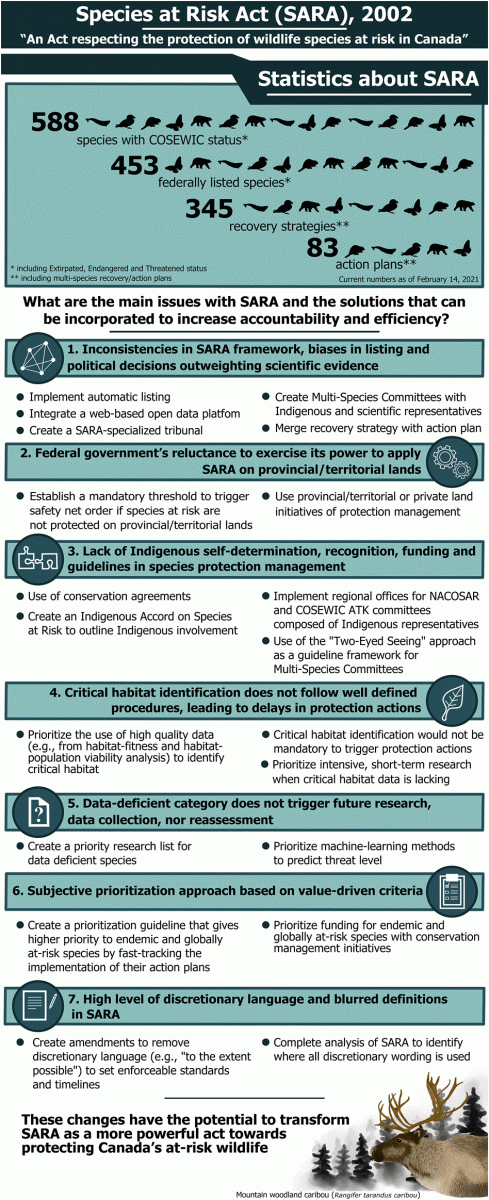
Abstract
Since the implementation of the Canadian Species at Risk Act (SARA) in 2003, deficiencies in SARA and its application have become clear. Legislative and policy inconsistencies among responsible federal agencies and the use of a subjective approach for prioritizing species protection lead to taxonomic biases in protection. Variations in legislation among provinces/territories and the reluctance of the federal government to take actions make SARA’s application often inefficient on nonfederally managed lands. Ambiguous key terms (e.g., critical habitat) and disregard for legislated deadlines in many steps impede the efficacy of SARA. Additionally, the failure to fully recognize Indigenous knowledge and to seek Indigenous cooperation in the species protection process leads to weaker government accountability, promotes inequity, and leads to missed opportunities for partnerships. New legislative amendments with well-defined and standardized steps, including an automatic listing process, a systematic prioritization program, and clearer demands (e.g., mandatory threshold to trigger safety net/emergency order) would improve the success of species at risk protection. Moreover, a more inclusive approach that brings Indigenous representatives and independent scientists together is necessary for improving SARA’s effectiveness. These changes have the potential to transform SARA into a more powerful act towards protecting Canada’s at-risk wildlife. (The graphical abstract follows.)
Graphical Abstract